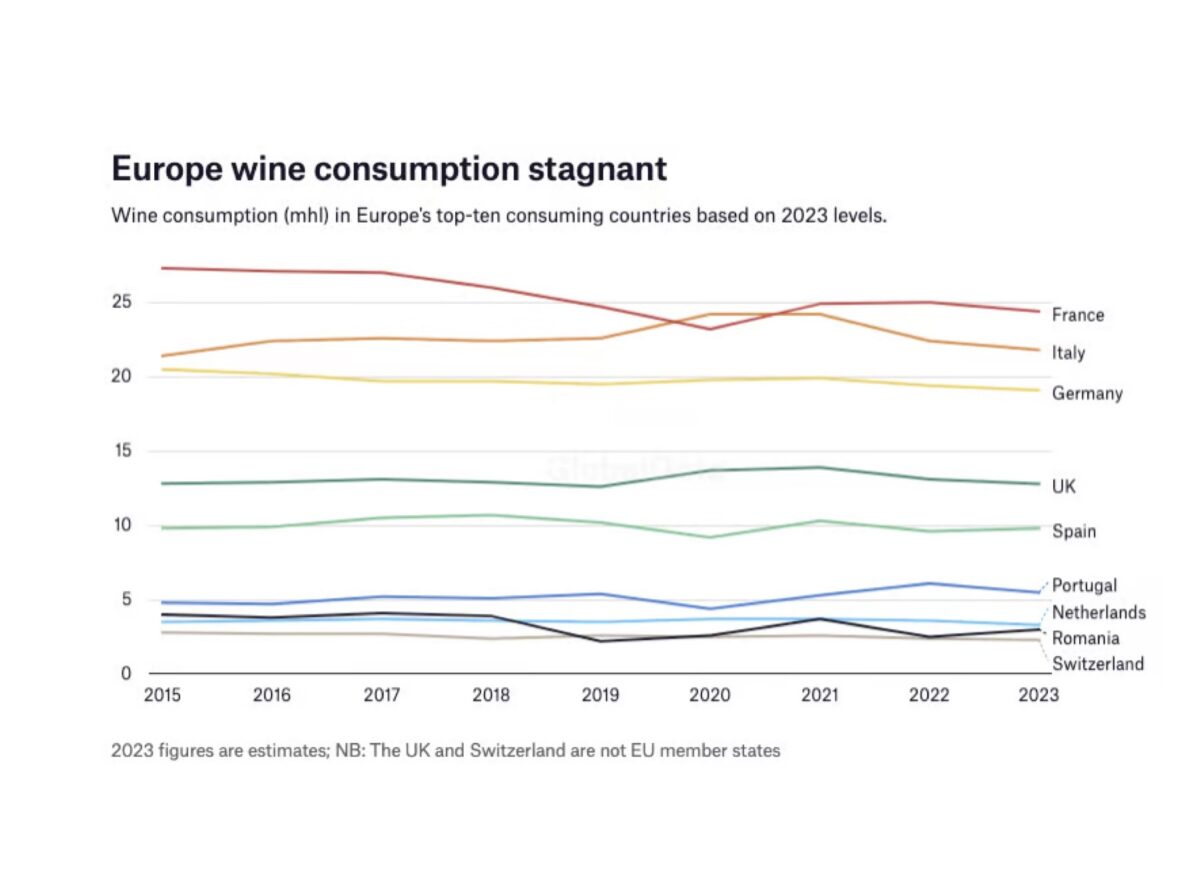
In 2023, EU member states accounted for 48% of global wine consumption, totalling 107 million hectolitres. This volume marked a slight decline of 1.8% compared to 2022. Nevertheless, this consumption level was over 5% below the decade-long average, as the industry faced several challenges.
Source: OIV